SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol
Exchange management information between network devices
- Each Managed Device, a host or a router, maintains a number of Management Information Bases (MIBs)
- Each managed device has an SNMP Agent to provide interface between MIBs and an SNMP Manager
- An SNMP manager, usually implemented in Network Management System (NMS), can work with multiple SNMP agents
- Uses well-known UDP port number 161/162 at the agent/manager
SNMP Message Format
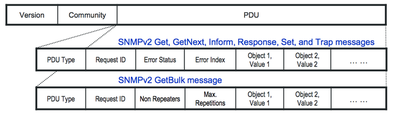
- Community Name
- Access scope for SNMP managers and agents
- A different community name will be discarded
- Protocol Data Unit (PDU) Type specifies the SNMP message type
- Request ID: match an SNMP request with the corresponding response
MIB (Management Information Bases)
A managed device maintains a large number of SNMP objects to store management information. The Structure of Management Information (SMI) defines the rules for describing management information and the data types used in SNMP.
- Tree Structure
- Each level of the tree consists of groups
- Each group has its name and the associated numerical identifier
- Leaves in the mib-2 subtree are MIB objects
Here is an example for MIB Tree Structure:
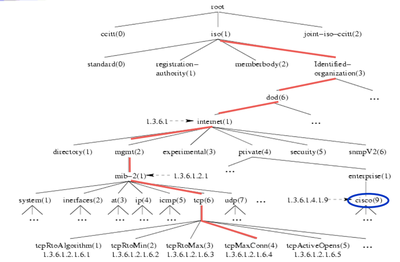
The leaf tcpMaxConn can be defined as 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.4 or iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib-2.tcp.tcpMaxConn.