DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Designed to dynamically configure TCP/IP hosts in a centralized manner from DHCP server.
Function
Configure parameters in a subnet dynamically
- IP Address, Subnet mask, default gateway IP address
Process
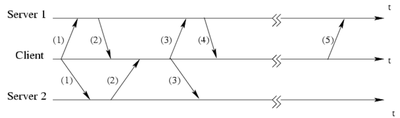
Here is a graph to show how DHCP works
-
A client first broadcasts a DHCP DISCOVERY message on its local physical network
- The message has 0.0.0.0 as the source IP address
- The message may be forwarded by relay agents to servers in other physical networks
-
Each server may respond with a DHCPOFFER message with an available network address in the Your IP Address field
-
The client may receives more than one DHCPOFFER messages
- It chooses one server from all responding servers based on the offered IP address and the lease duration.
- The client then broadcasts a DHCPREQUEST message with the Server Identifier option to indicated the selected server.
-
When the DHCPREQUEST message is received, only the chosen server responds with a DHCPACK message carrying a full set of configuration parameters to the client.
- When the client receives, it checks the parameters and configures its TCP/IP modules using the parameters.
- The message specifies the duration of the lease. When the lease expires, the client may ask the server to renew it. Otherwise, the address will be put back in the pool or assigned to other hosts.
-
(When two DHCP servers are used) The client may send a DHCPRELEASE message to the server to relinquish the lease on the network address.
DHCP Message Format
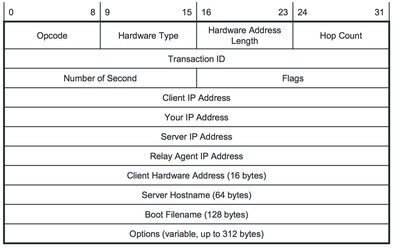
- Opcode: 1 – a boot request from client; 2 – a boot reply from server
- Hardware Address Type
- The value is 1 for an Ethernet MAC address
- Hop count
- Optionally used by relay agents
- A DHCP relay agent is a host or router that forwards DHCP messages between DHCP clients and servers
- Transaction ID
- Randomly assigned to link requests and replies between a client and a server
- Client HW address
- The hardware address of the client
- For an Ethernet address, the first 6 bytes are filled and the remaining bytes are set to 0
- Server hostname: Hostname of the DHCP server
- Boot filename
- Use in a DHCPOFFER message to specify the fully qualified, null terminated path name of a file to bootstrap from
DHCP Relay Information Option
Assign IP address based on its location. DHCP client in a Residential Gateway (RG) will send a DHCP request to an ISP Broadband Network Gateway. A network access node, such as an IP DSLAM, aggregates traffic from many users.